What is the difference between MCB and RCD?
Differences Between MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) and RCD (Residual Current Device)
MCBs and RCCBs (often known as RCDs) serve distinct protective functions in an electrical installation. Here is a detailed comparison of their differences.
1. Primary Function
-
MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker): Its core function is to provide overload and short-circuit protection. It automatically trips (switches off) when the circuit current exceeds its rated value for a prolonged period (overload) or when a sudden, massive current surge occurs (short circuit). This protects the wiring and connected equipment from damage due to excessive heat or electrical faults.
-
RCD aslo named RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker): Its primary purpose is earth leakage protection. It detects an imbalance between the live and neutral currents, which indicates that current is leaking to earth, for example, through a person (electric shock) or a faulty appliance. Upon detecting such a leakage, it trips rapidly to prevent electric shock hazards.
2. Application Scenarios
-
MCB: Suitable for general circuit protection in various settings such as homes, offices, and factories. They are commonly used for circuits supplying lighting, sockets, and small appliances.
-
RCCB: Essential for areas with a higher risk of electric shock due to moisture or where greater personal safety is required. Typical applications include kitchens, bathrooms, swimming pools, as well as public facilities like hospitals, schools, and kindergartens.
3. Structure and Appearance
-
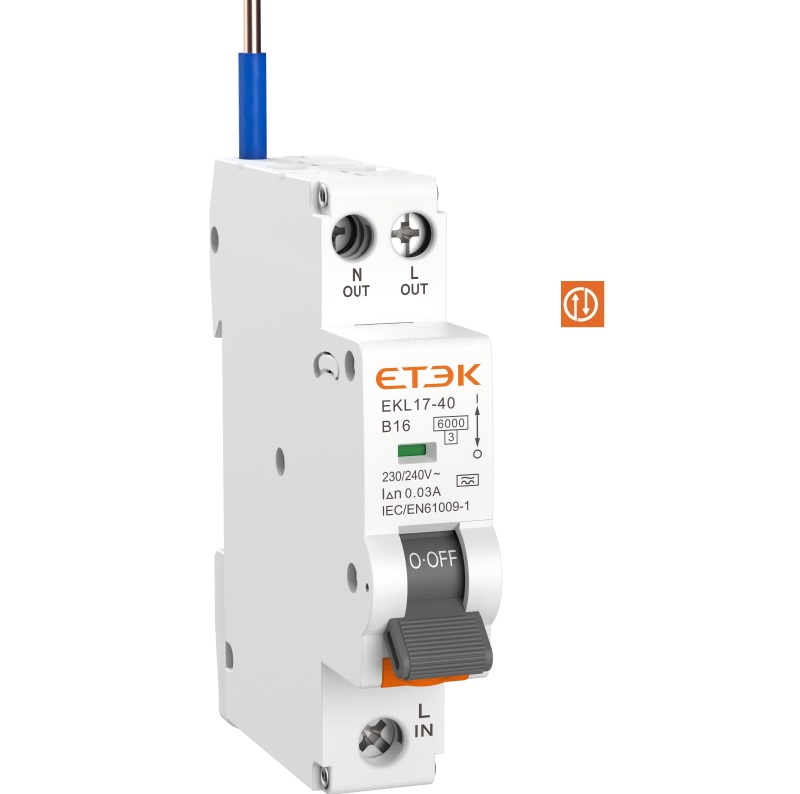
MCB: Typically features only an operating handle for manually switching the circuit ON and OFF and resetting it after a trip.
-
RCCB: In addition to an operating handle, it is equipped with a test button (usually marked 'T'). This button allows for regular manual testing to verify that the leakage protection mechanism is functioning correctly.
4. Key Technical Parameters
-
MCB: Key specifications include Rated Current (In), Rated Voltage (Ue), and Breaking Capacity (Icn).
-
RCCB: Includes all the parameters of an MCB but adds critical leakage-specific ratings: Rated Residual Operating Current (IΔn) and Rated Residual Non-operating Current (IΔno). A common standard for personal protection is an IΔn of 30mA, with a maximum tripping time of 0.1 seconds at that leakage current.
5. Installation and Usage Requirements
-
MCB: Correct installation is vital, ensuring proper wiring (live and neutral) to the designated terminals for normal operation.
RCCB: After installation, it is crucial to perform regular functional tests by pressing the test button periodically (e.g., monthly). If the RCCB trips due to a leakage fault, the cause (e.g., a faulty appliance) must be identified and eliminated before the breaker can be manually reset.
6. Comparison Summary: MCB vs. RCD
An MCB is designed to protect the electrical installation (wires and appliances) from excessive current. An RCCB is designed to protect people from electric shock. They are often used together in modern electrical systems for comprehensive safety.
| Feature | Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) | Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB/RCD) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Circuit Protection: Protects electrical wiring and equipment from damage caused by overcurrents. | Personal Protection: Protects people from electric shock caused by earth leakage. |
| Protects Against | Overload & Short Circuit | Earth Leakage (Ground Fault) |
| Operating Principle | Trips when the current flow exceeds a safe threshold for a duration (thermal-magnetic action). | Trips when it detects an imbalance between the live and neutral currents, indicating current is leaking to earth. |
| Key Parameters | Rated Current (e.g., 16A), Breaking Capacity (e.g., 6kA) | Rated Current, Rated Residual Current (e.g., 30mA), Trip Time (e.g., ≤0.1s) |
| Visual Identification | Typically features only an operating handle (ON/OFF switch). | Features an operating handle and a test button (marked 'T') for regular function checks. |
| Common Applications | General-purpose circuits in homes, offices, and industries (e.g., lighting, power sockets, air conditioners). | Areas with a high risk of electric shock due to moisture or sensitive use (e.g., bathrooms, kitchens, swimming pools, construction sites). |
| Installation & Maintenance | Requires correct installation. Functional testing is not routinely required by the user. | Must be tested regularly by pressing the 'T' button (e.g., monthly) to ensure the protection mechanism works. The fault must be cleared after a trip before resetting. |
7. The next product after MCB & RCD:
RCBO: (Residual Current Breaker with Overcurrent Protection)
AFDD:(Arc Fault Detection Devices), represent a new type of electrical protection equipment. Their primary function is to detect and prevent arc faults in electrical circuits, thereby effectively reducing the risk of electrical fires,now AFDD normally integreted with RCBO,makes it with overeload,short circuit,erath leakage,and fire protection.























